A Low Residue Diet is often recommended when your digestion needs a break. If frequent bathroom trips, cramps, or discomfort disrupt your day, this eating plan can help restore balance. By limiting foods low in fiber, the diet reduces waste inside the gut and supports digestive tract health.
Doctors commonly suggest it for short periods to reduce bowel movements and ease symptoms linked to sensitive digestion. Many people follow a low fiber diet like this during medical prep or flare-ups to achieve diarrhea and bloating relief. When chosen carefully and followed for the right duration, a low residue diet can calm irritation, improve comfort, and help your digestive system recover without unnecessary strain.
Table of Contents
What Is a Low Residue Diet? (Simple Explanation)
A low residue diet limits foods low in fiber to decrease waste in your intestines. “Residue” means undigested material in stool and residue left after digestion. Less residue means less strain.
This approach aims to reduce bowel movements and irritation. By choosing easy to digest foods, your gut gets a break, which supports bowel irritation reduction and comfort during flare-ups.
How Does a Low Residue Diet Work in the Digestive System?
Fiber adds bulk. Bulk increases stool volume. For sensitive guts, that can trigger gas cramps and bloating. A low fiber diet reduces bulk and promotes digestive system rest.
With less bulk, the frequency and size of stools drop. This helps gastrointestinal symptom relief, improves bowel movement control, and lowers intestinal obstruction risk during healing.
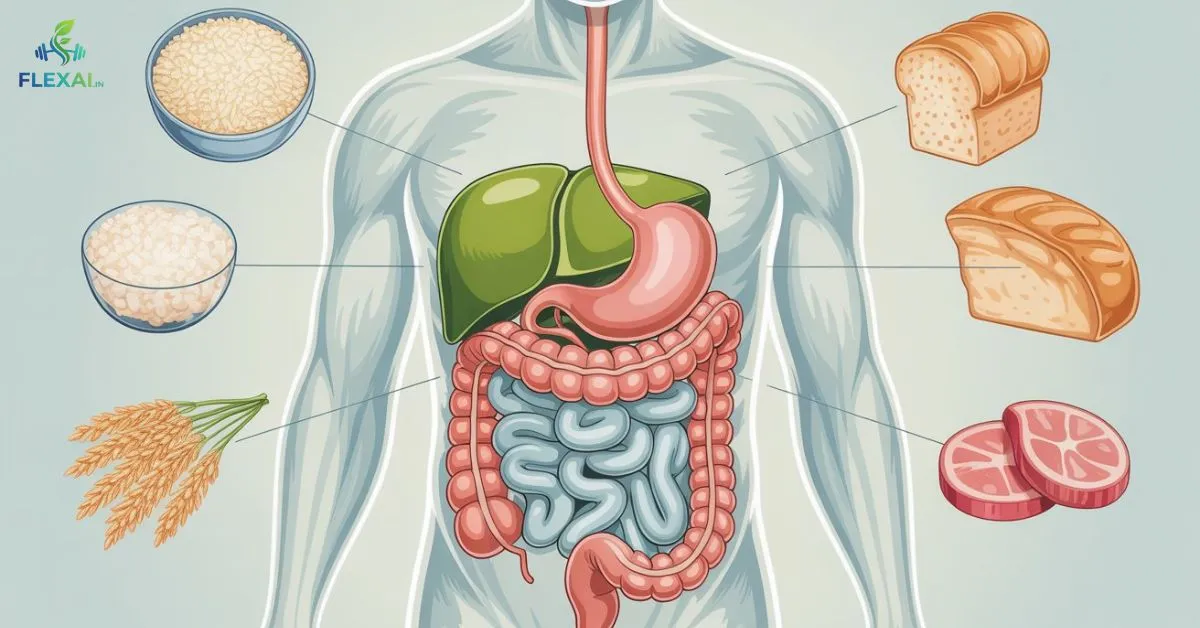
Who Should Follow a Low Residue Diet?
Doctors recommend this digestive conditions diet for people with inflammatory bowel disease diet needs, including Crohn’s disease diet and ulcerative colitis diet plans. It also helps during diverticulitis diet flare-ups.
It’s common before procedures. As a colonoscopy preparation diet or bowel surgery diet, it reduces residue and eases prep. It’s also useful as a post-surgery digestive diet.
Medical Conditions That Benefit Most
This plan supports gut inflammation management during active symptoms. It’s not a cure. It’s a short-term therapeutic diet used for control and recovery with doctor recommended diet oversight.
Low Residue Diet Benefits (Why Doctors Recommend It)
The biggest win is diarrhea and bloating relief. Less residue means fewer triggers. Many notice calmer digestion within days.
It also helps digestive flare-up prevention and safer procedures. By reducing bulk, it lowers stress on healing tissue and supports recovery.
Low Residue Diet Foods List (What You Can Eat)
Focus on easy to digest foods and refined carbohydrates that pass gently. Think refined grains digestion, smooth textures, and cooked options.
Safe choices include skinless seedless fruits, tender cooked meats, and gentle dairy if tolerated. Fluids matter too. Prioritize clear liquids and hydration.

Low Residue Diet Foods to Avoid (What Not to Eat)
Avoid items that increase bulk. The low residue diet foods to avoid list includes whole grains, nuts, seeds, legumes, raw produce, and spicy foods.
These foods raise residue and can worsen symptoms. Skipping them supports comfort and healing during sensitive periods.
Low Residue Diet Menu Plan (1-Day & 7-Day Sample Plan)
A low residue meal plan keeps meals simple and spaced. Breakfast might include eggs and white toast. Lunch can be chicken with white rice. Dinner works well with fish and mashed potatoes.
Here’s a simple reference for portions and balance within a low residue diet menu:
| Meal | Example | Why It Works |
|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | Scrambled eggs, white toast | Low bulk, gentle |
| Lunch | Chicken, white rice | Easy digestion |
| Dinner | Fish, mashed potatoes | Soft texture |
How to Cook on a Low Residue Diet (Easy Cooking Tips)
Cooking style matters. Use steaming, poaching, simmering, or microwaving. These methods keep foods soft and easy to digest.
Avoid drying methods. Tough textures slow refined grains digestion and irritate the gut. Keep flavors mild and textures smooth.
Meal Prep Tips for Digestive Comfort
Cook ahead and reheat gently. Moisture helps digestion. Follow dietitian guidance if symptoms persist or needs change.
Low Residue Diet for Colonoscopy Preparation
As prep for colonoscopy, this diet reduces residue so the bowel clears well. Doctors prefer it over liquids for comfort and tolerance.
Follow timing carefully. Switch days before the procedure and stop solid foods when instructed. This supports accurate results.
Pros and Cons of a Low Residue Diet
Pros include symptom control and comfort. It supports healing and reduces stress on inflamed tissue.
Cons matter too. Long use raises nutrient deficiency risk due to low fiber. That’s why it’s a short-term medical diet.
Low Residue Diet vs Low Fiber Diet (Key Differences)
A low fiber diet focuses on fiber numbers. A low residue diet goes further by limiting foods that leave waste.
Both overlap, but residue considers digestion outcome. Doctors choose based on symptoms and goals.
How Long Should You Follow a Low Residue Diet?
Most people follow it briefly. Days or weeks are typical. Longer use requires supervision.
Transition slowly. Reintroduce fiber with care. Always follow doctor recommended diet plans and seek dietitian guidance.

Final Thoughts
A low residue diet can calm your gut when symptoms peak or procedures loom. It supports healing, comfort, and control. Use it short term. Listen to your body. Work with professionals. When used wisely, it’s a powerful tool for digestive relief.
FAQ
What foods are in a low-residue diet?
Low-residue foods include white bread, white rice, eggs, tender meats, cooked vegetables without skin, ripe bananas, and clear fluids.
What meals can I make on a low-residue diet?
Simple meals like scrambled eggs with toast, baked chicken with white rice, or fish with mashed potatoes work well.
What can I eat on a low-residue diet before a colonoscopy?
You can eat white rice, eggs, skinless chicken, yogurt, and clear soups, then switch to liquids as advised by your doctor.
Are eggs a low residue food?
Yes, eggs are low in residue and easy to digest, making them safe on a low-residue diet.
What is okay to eat 3 days before a colonoscopy?
Three days before, eat low-residue foods like white bread, eggs, lean meats, peeled fruits, and avoid seeds or whole grains.